Safeguarding Accounts: Your Key to Financial Security in 2025


Did you know that 15% of fintech companies in 2024 lost client trust due to inadequate protection of their funds, according to the FCA? In a world where the fintech market grows by 25% annually, safeguarding client assets is not just a regulatory requirement but a cornerstone of competitiveness. Safeguarding is a tool that enables fintechs to mitigate risks of PSP insolvency, ensure compliance with FCA and PSD2 standards, and build client trust. This article explores what safeguarding is, why it matters, how it differs from operational accounts, and how to implement it for your business.
With stricter ECB regulations, including a ban on using central banks for safeguarding from April 2025, fintechs face new challenges. Meanwhile, technologies like AI monitoring and open banking unlock opportunities for secure, fast transactions. According to Visa, robust fund protection can boost client trust by 30%.
What is a Safeguarding Account and Why is it Important?
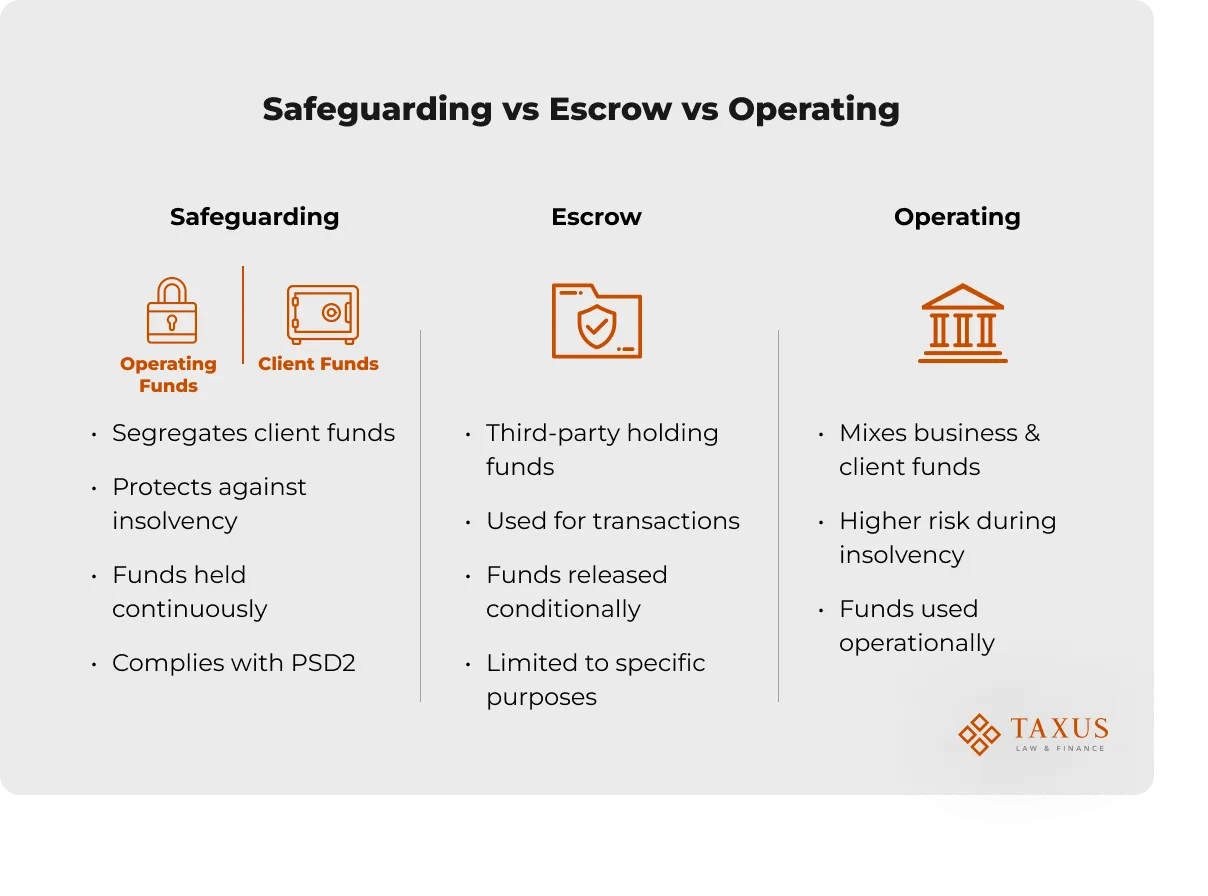
A safeguarding account is a segregated account designed to protect client funds in fintech companies from risks like PSP insolvency or misuse. It isolates client assets from operational accounts, a requirement of regulators like the FCA and PSD2 in the EU. This tool is not just a technical formality—it’s the foundation for building client trust and ensuring compliance with international standards.
Safeguarding in 2025
With technological advancements, safeguarding is gaining new significance. AI-powered anomaly monitoring reduces fraud risks by 20%, according to fintech experts. For instance, AI algorithms used by Revolut detect suspicious transactions in milliseconds. Open banking, meanwhile, enables fast transactions via API integration, as seen in payment systems like Stripe. In Europe, ECB regulation (Regulation (EU) 2024/886) mandates that EMIs and PIs transfer excess funds to commercial banks by April 2025, making safeguarding a must-have for compliance.
Applications Across Fintech Niches
Safeguarding is critical for neobanks (e.g., Monzo), e-wallets (e.g., PayPal), and crypto platforms (e.g., Coinbase). For example, crypto platforms use safeguarding to shield client assets from market volatility, enhancing their appeal. According to Deloitte, 80% of neobanks in 2024 adopted safeguarding, attracting 15% more clients.
Why Safeguarding Matters
First, it boosts client trust: 70% of users choose fintechs with robust fund protection, per Visa’s 2025 data. Second, it minimizes non-compliance risks—FCA fines for inadequate safeguarding can reach €200,000. Third, it saves costs: segregated accounts reduce audit and insurance expenses
2. Safeguarding vs. Traditional Bank Accounts: Key Differences
A safeguarding account differs from traditional bank accounts in its technical approach to protection. Safeguarding isolates client funds (segregation), protecting them in case of PSP insolvency, while traditional accounts often commingle funds with operational ones, increasing loss risks. For example, ECB policy (effective July 2024) requires segregation for payments only, with excess funds in commercial banks, as outlined in Regulation (EU) 2024/886. Similarly, FCA and PSD2 enforce strict client asset isolation rules.
In contrast, escrow accounts, often confused with safeguarding, are used for temporary fund holding (e.g., in real estate) but don’t meet PSD2 requirements for fintech payments. Safeguarding ensures ongoing isolation and protection from operational risks.
Key Differences in a Table
| Criterion | Safeguarding Account | Traditional Bank Account |
| Protection | Fund isolation, insolvency protection | Commingling, risk of loss |
| Regulation | PSD2/EBA/FCA: mandatory segregation | Standard banking rules, no segregation |
| Risks | Low, enhanced by AI monitoring | High during PSP insolvency |
| Costs | Initial integration, saves on fines | Low, but high fine risks |
Case 1: In November 2024, the Central Bank of Ireland fined BlueSnap Payment Services Ireland Ltd €324,240 for breaching safeguarding rules. The company held client funds in a regular operational account, commingling them with its own. This increased the risk that, in case of insolvency, client funds would be used to cover company debts instead of being returned to clients.
Case 2: Neobank Monzo, by contrast, uses safeguarding accounts effectively, avoiding losses during FCA audits in 2024, strengthening its reputation, and attracting 10% more clients.
Safeguarding could have prevented BlueSnap’s losses. Check your account readiness.
3. How to Open a Safeguarding Account: Requirements and Process
Opening a safeguarding account is a structured process ensuring compliance and client fund protection. Requirements include an EMI/PI license, selecting a bank partner with tailored solutions (e.g., multi-currency or SEPA Instant), and regular audits. From April 2025, ECB regulation (Regulation (EU) 2024/886) prohibits EMIs from using central banks for safeguarding, requiring excess funds in commercial banks.
Key Requirements:
- EMI/PI license (per PSD2).
- Bank partner offering solutions like multi-currency accounts or SEPA Instant (e.g., Magnetiq Bank, ClearBank).
- Audits and controls (reconciliations, KYC/AML, internal policies).
- Quarterly reporting, as mandated by FCA for PSPs.
Checklist: 5 Steps to Safeguarding:
- Assess Regulations: Verify FCA/PSD2 requirements (e.g., segregation for payments only, excess in commercial banks).
- Choose a Bank: Select partners like Magnetiq Bank or ClearBank, offering multi-currency accounts and SEPA Instant.
- Open the Account: Submit documents (EMI/PI license, KYC: articles of association, financial statements, AML policy) and integrate APIs for automation.
- Integrate Technology: Add AI monitoring (e.g., Visa’s fraud detection systems) and open banking APIs (e.g., Stripe).
- Conduct Audits: Perform compliance checks every six months to avoid fines (€200,000 for non-compliance, per FCA cases).
Case Study: An investment platform was fined £1.12M by the FCA because its automated “sweep” settings moved client funds from a segregated account to an unprotected operational account during the day. Even though funds were segregated by day’s end, this intra-day movement violated safeguarding rules. Safeguarding requires diligent monitoring, even for automated processes.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a safeguarding account in fintech?
This is a separate (segregated) account where the funds of the payment company’s clients (PSP, EMI, PI) are stored. Its main purpose is to guarantee that the clients’ money will be returned even in the event of the company’s bankruptcy. For example, in the UK, the FCA requires licensed PSPs to store funds in a safeguarding account, separate from the operational ones.
How does safeguarding differ from insurance?
Safeguarding isolates funds to prevent loss (e.g., during insolvency), while insurance compensates losses post-event. Safeguarding is a PSD2 requirement; insurance is optional.
Which regulations govern safeguarding?
ECB (Regulation (EU) 2024/886: April 2025 deadline), PSD2 in the EU, and FCA in the UK. For instance, FCA mandates quarterly reporting for PSPs to ensure compliance.
How does AI help in safeguarding?
AI monitors anomalies in real-time, reducing fraud risks by 20%, as seen in Visa’s systems. PayPal, for instance, uses AI to detect suspicious transactions instantly.
Що означає ECB regulation 2025 для EMIs/PIs?
З квітня 2025 EMIs не можуть використовувати central banks для safeguarding, з excess funds у commercial banks, що вимагає нових банківських партнерств.
What does ECB regulation 2025 mean for EMIs/PIs?
From April 2025, EMIs cannot use central banks for safeguarding, requiring excess funds in commercial banks, necessitating new banking partnerships.
What happens after setting up a safeguarding account? Is it done?
Not quite. To maintain compliance, your business must undergo an independent annual audit to confirm that safeguarding processes are effective and client funds are protected. The audit should demonstrate:
An up-to-date safeguarding systems and controls manual;
Detailed records explaining the rationale behind safeguarding decisions;
Full compliance with safeguarding obligations under the Payment Services Regulations (PSRs), as required by the FCA.
Conclusion: Protect Your Business with Safeguarding Accounts
A safeguarding account is key to securing client funds, ensuring ECB/PSD2/FCA compliance, and fostering trust. It stands apart from traditional accounts through segregation, and the setup process is straightforward with the right partner. With AI, open banking trends, and the ECB’s April 2025 deadline, safeguarding is a must-have for fintechs.
References
- Central Bank of Ireland. The Central Bank takes enforcement action against BlueSnap Payment Services Ireland Limited for safeguarding failures. Press release, 21 November 2024. Available at: https://www.centralbank.ie/news/article/the-central-bank-takes-enforcement-action-against-bluesnap-payment-services-ireland-limited-for-safeguarding-failures. Accessed 3 September 2025.
- Addleshaw Goddard LLP. Official website. Available at: https://www.addleshawgoddard.com/en/. Accessed 3 September 2025.

Looking for a reliable payment processing system?
Order selection of a payment solution.